 Before you fly, review the steps below to make sure your first flight is a success.
December 22, 2016
Before you fly, review the steps below to make sure your first flight is a success.
December 22, 2016 – Last Christmas the FAA estimated that over 1 million individuals received a drone as a gift. This year, that number is expected to rise.
The continued popularity of drones, coupled with increased selection and lower prices, means a fair share of holiday gifts will include a drone.
However, with that gift comes responsibility.
So, what exactly do first time flyers need to do before taking that drone out for a spin? Read on to find out.
Register your drone
Whether a drone is for commercial purposes or simply for fun, it must be
registered with the FAA. Any drone weighing between 0.55 lbs. and 55 lbs. must be registered. The registry helps create accountable flyers and safer skies.
Any time you fly, make sure you bring your registration information with you. Think of it like a fishing license, it doesn’t do you much good sitting at home. Registration costs $5 and it is a much cheaper than paying a fine up to $27,500 in civil penalties for flying unregistered. Unregistered drones, coupled with criminal penalties, are far steeper and could cost an operator up to $250,000.
Save yourself the stress and risk; take 5 minutes, spend $5 and
register your drone with the FAA.
Know the rules
The rules for hobbyist drone operators are quite simple:
- Keep it low – never fly above 400 feet
- Keep it in sight – keep visual contact of your drone at all times
- Keep it away – never fly over people
- Keep it legal – fly according to community-based guidelines
- Give notice – if you’re flying within 5 miles of an airport
As for commercial flyers, they have additional requirements and guidelines they must follow. Plus, there are tests they must pass and licenses they must secure before operating their vehicle.
Know your airspace
Those open skies aren’t as open as you may think. In fact, our airspace is crowded with all types of air traffic – commercial and recreational, alike. It is your responsibility to understand what is going on above and around the area you are flying your drone.
It is good practice to stay away from dense, urban areas. Dense areas are littered with trouble spots for drones: powerlines, pedestrians, private property, and moving vehicles…to name a few. Keep it safe, fly in deserted areas far from the city. Also, remember to stay at least 5 miles away from an airport.
Know the weather
That drone may not be as rugged as you think. Keep your equipment safe, take a moment to look at weather conditions. High winds? Low visibility? Air pressure changes? These factors, and more, can significantly impact your drone’s performance…as well as yours, as a novice flyer. For instance, flying in stiff winds can impact the life of your battery and, thus, decrease flight endurance.
Know your limits
As you may guess, it takes a lot of time and a lot of practice to become a proficient drone operator. Though the drone may come out of the box ready-to-fly, it doesn’t mean the operator has the skills to keep it from crashing.
If you’re just starting out, take your time. Get familiar with your drone. Read the manuals. Become comfortable in your operational controls. Practice take-off and landing before venturing out. Once you’re ready for a longer flight, keep it safe…follow the recommended guidelines.
As the skies continue to fill with drone traffic, the actions of individual operators are sure to determine the pace and integration of this technology into daily life. Follow the rules and enjoy!
 Legislation introduced in the state of Washington aims to limit drone interference for some very special residents…an endangered population of Orcas.
These Orcas, also known as the southern resident killer whales, are the smallest of four resident communities within the area. It is the only killer whale population listed as endangered by the U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service. In addition, they are protected under the Endangered Species Act.
The proposed bill requires drone operators to maintain a 200-yard buffer, in all directions, from any southern resident killer whales. This buffer already applies to boats, vessels and other objects that might encroach on the animals.
However, the existing law was unclear as to whether or not the line other objects applied to drones and other sUAS.
Legislation introduced in the state of Washington aims to limit drone interference for some very special residents…an endangered population of Orcas.
These Orcas, also known as the southern resident killer whales, are the smallest of four resident communities within the area. It is the only killer whale population listed as endangered by the U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service. In addition, they are protected under the Endangered Species Act.
The proposed bill requires drone operators to maintain a 200-yard buffer, in all directions, from any southern resident killer whales. This buffer already applies to boats, vessels and other objects that might encroach on the animals.
However, the existing law was unclear as to whether or not the line other objects applied to drones and other sUAS.

 In a world increasingly reliant on technology to function, cyber security has quickly become an important issue.
Which begs the question, how safe is your drone from a hacker attack?
Experts predict that the hijacking of drones may be one of the next big cyber threats; which raises the potential for worrying possibilities.
In its 2017 Threats Predictions Report, McAfee Labs listed drone hijackings as one of 14 cyber security issues for the coming year. The report noted that attacks against hardware – such as mobile devices and drones – would increase in 2017.
In a world increasingly reliant on technology to function, cyber security has quickly become an important issue.
Which begs the question, how safe is your drone from a hacker attack?
Experts predict that the hijacking of drones may be one of the next big cyber threats; which raises the potential for worrying possibilities.
In its 2017 Threats Predictions Report, McAfee Labs listed drone hijackings as one of 14 cyber security issues for the coming year. The report noted that attacks against hardware – such as mobile devices and drones – would increase in 2017.
 Before you fly, review the steps below to make sure your first flight is a success.
December 22, 2016 – Last Christmas the FAA estimated that over 1 million individuals received a drone as a gift. This year, that number is expected to rise.
The continued popularity of drones, coupled with increased selection and lower prices, means a fair share of holiday gifts will include a drone.
However, with that gift comes responsibility.
So, what exactly do first time flyers need to do before taking that drone out for a spin? Read on to find out.
Before you fly, review the steps below to make sure your first flight is a success.
December 22, 2016 – Last Christmas the FAA estimated that over 1 million individuals received a drone as a gift. This year, that number is expected to rise.
The continued popularity of drones, coupled with increased selection and lower prices, means a fair share of holiday gifts will include a drone.
However, with that gift comes responsibility.
So, what exactly do first time flyers need to do before taking that drone out for a spin? Read on to find out.

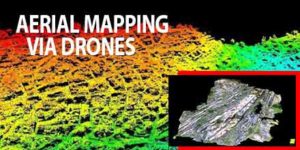 The surveying and mapping industry has used photogrammetry and LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) for many years, Questions over which is best have gone on for just as long.
Choosing between photogrammetry and LiDAR is not a case of which offers superior technology but, rather, which is better suited for the surveying purposes required. Professionals working in the sector understand that both have their benefits.
Photogrammetry uses pictures to take measurements whereas LiDAR uses lasers and light to do the same. For mapping and surveying bare earth regions, photogrammetry is a great choice. But for areas with heavy vegetation or other obstructions in the way of the site being surveyed, LiDAR provides the best fit.
The surveying and mapping industry has used photogrammetry and LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) for many years, Questions over which is best have gone on for just as long.
Choosing between photogrammetry and LiDAR is not a case of which offers superior technology but, rather, which is better suited for the surveying purposes required. Professionals working in the sector understand that both have their benefits.
Photogrammetry uses pictures to take measurements whereas LiDAR uses lasers and light to do the same. For mapping and surveying bare earth regions, photogrammetry is a great choice. But for areas with heavy vegetation or other obstructions in the way of the site being surveyed, LiDAR provides the best fit.
